How Your Electricity Service Works in Texas
How does electricity make its way to your home? Our guide explains the different steps that are involved in your electricity service
With the electricity markets in Texas deregulated, your electricity service can be broken down into three main steps:
Generation
Did you know? Texas has the highest electricity demand in the US. According to the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT), the state consumed over 340 billion kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity in 2014.
Electricity in Texas comes from a mix of renewable and non-renewable sources. With over 10% of electricity in the ERCOT grid coming from wind generation, Texas is the largest producer of wind power in the country. However, the majority of Texas energy generation comes from fossil fuels: in 2014 36% of Texas electricity generation came from coal and 41.1% from natural gas.
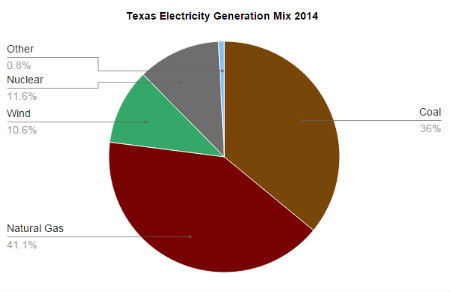
Source: ERCOT
There are over 550 generating units in Texas, with over 74 000 MW capacity for peak demand. As part of deregulation of the Texas electricity system, electricity generators are free to sell electricity on a wholesale power market within the ERCOT service territory.
ERCOT is the independent systems operator for the majority of Texas, and manages the electricity system for 75% of the land area in Texas (90% of the state's power load). It has four primary activities:
Operating the wholesale market upon which power is bought and sold
Ensuring open access to transmission within its territory
Long-term planning for reliability
Operating the retail switching process
Transmission and Distribution
After electricity is generated, it travels along high-voltage lines across the province to local transformers. Once it reaches the local transformers, its voltage is reduced to be suitable for local distribution. It then travels along local distribution lines to reach your home.
As it doesn't make sense (economic or otherwise) to have competing electricity transmission and distribution wires in a given area, this part of the electricity system has not been opened to competition. There are five transmission and distribution utilities (TDUs) operating in the ERCOT territory. They operate as regulated monopolies, and have exclusive right to provide service within their service territories. Their tariffs are approved by the Public Utilities Commission of Texas and are updated twice a year. TDUs in the ERCOT area are required to provide access to their wires to all retail electric providers on a non-discriminatory basis under standard terms and conditions that have been approved by the PUC.
Your local transmission & distribution utility is responsible for delivering electricity, maintaining and repairing the local network. You should contact them in the event of an electrical emergency or power outage. Find out more about the TDUs in Texas.
Retail
The final stage of the electricity system is when it reaches your home. While your local TDU is responsible for delivering your power, you must purchase your electricity supply from a retail electricity provider (REP). Your chosen REP is your first point of contact for most questions about your electricity. Along with purchasing power on your behalf, they are responsible for paying the charges associated with power transmission & delivery to the relevant utility, for providing you with customer service, for and billing charges associated with your power consumption.
Find out about retail electricity providers in Texas.
Not in the ERCOT Service Area?
If you receive your electricity from your municipality or from a utility cooperative, you are not in the ERCOT service area and do not have a choice of retail electricity provider. Instead, your municipality or utility cooperative is responsible for all three steps of the electricity service system.
