National Grid electricity & gas bill example in New York State
Updated on
min reading
National Grid has a specific bill format for electricity & gas. Here is an explanation of a typical National Grid bill.
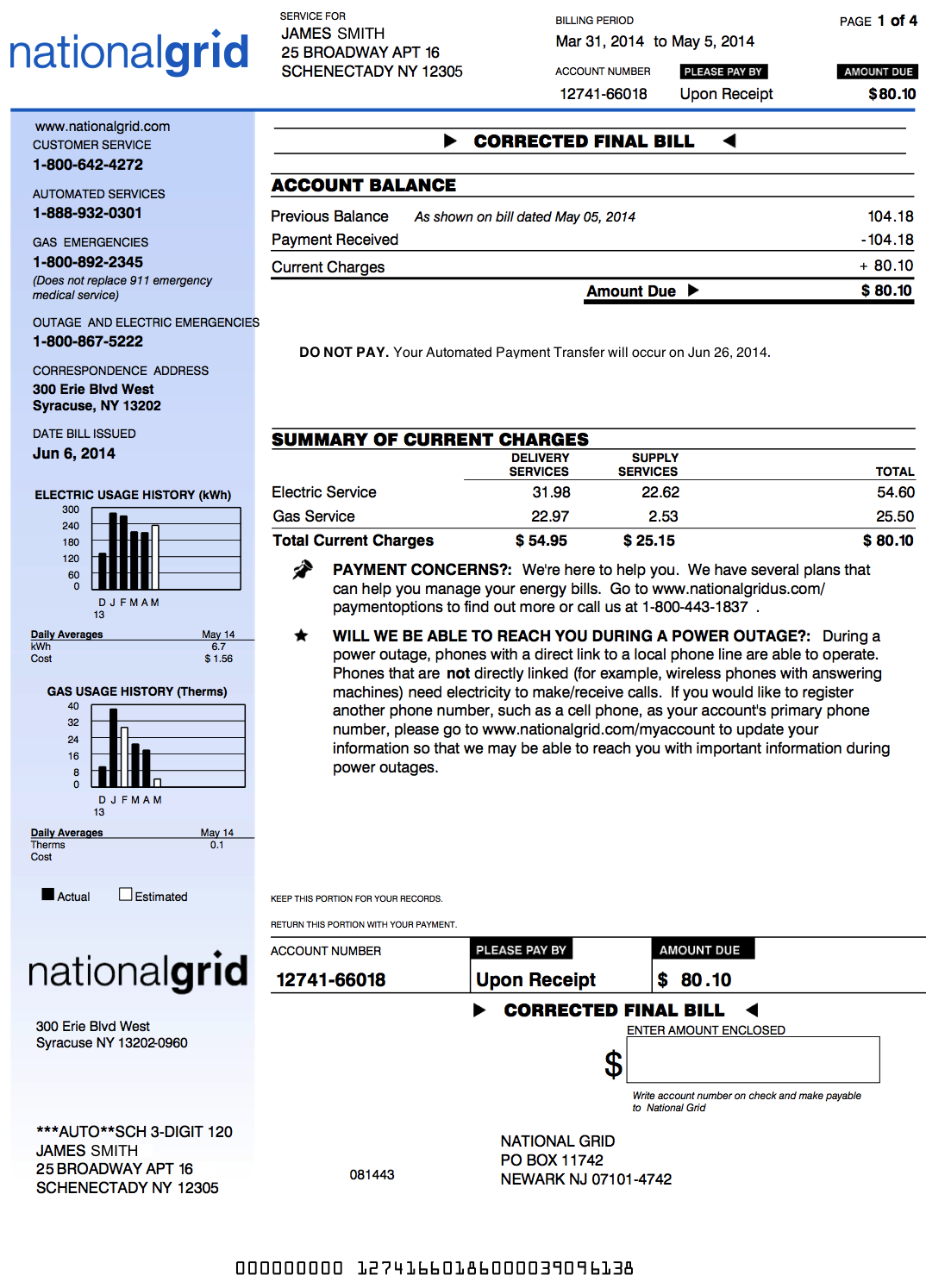
Example of a 2014 National Grid bill - page 1
Account information:
- Account number, customer address, billing period, account number, amount due.
Account balance
- Previous balance: Charges from previous bills (here a bill from May 5th, 2014).
- Payment received: Payment last received by National Grid for the payment of the previous bill. If the bill has been paid in full, this will be equal to the previous balance.
- Current charges: These are the charges for the current bill.
- Amount due: This will be equal to the current charges if the previous bill has been paid in full.
- "Do not pay": Depending on your payment method, a different message can appear here describing your next actions for bill payment.
- Message center: Since the customer did not pay his/her bill the previous month (the $207.86 outstanding balance for previous charges), an "adjustment" charge of $3.12 (1.5% of $207.86) has been added to the current bill.
Summary of current charges
- This summary divides the charges in the electric and gas service, as well as the delivery and supply service.
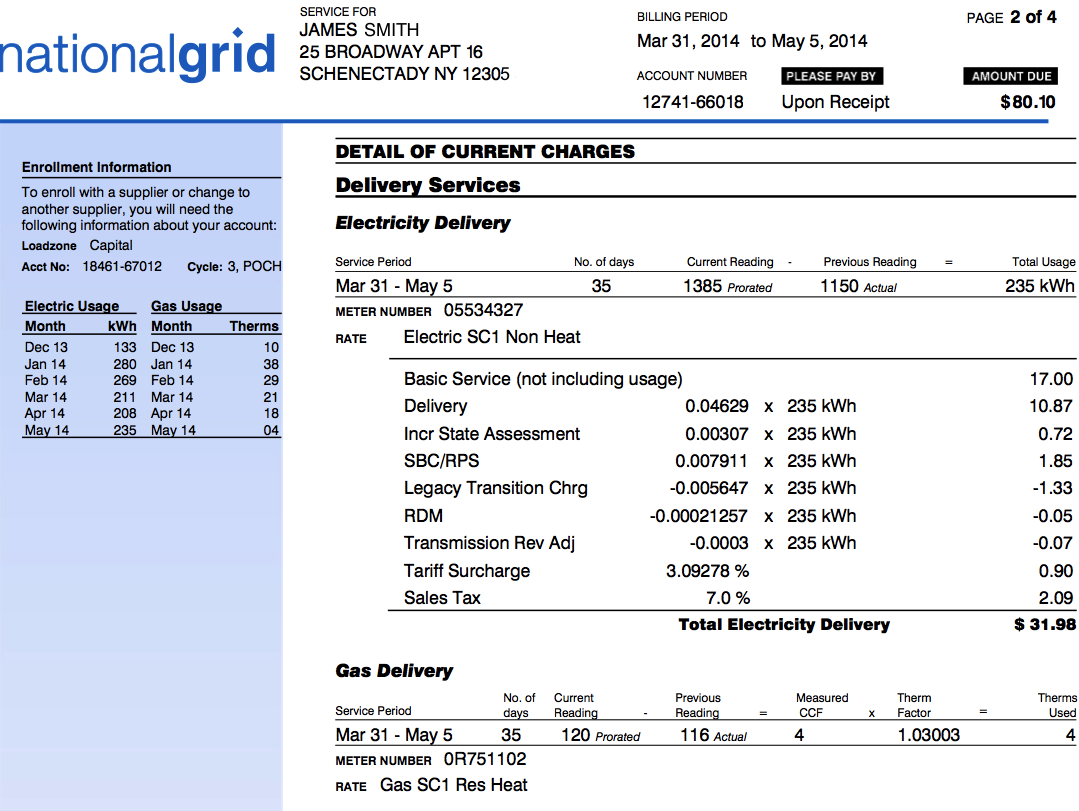
Example of a 2014 National Grid bill - page 2
Left column:
- This column gives you information about your monthly electricity and gas usage.
Delivery services:
Electricity delivery
- Meter information: This resumes the meter reading: dates of current and last meter reading and number of days, kWh shown on current and last meter reading and number of kWh.
- Rate: Electric SC1 Non Heat: This describes your rate plan. You can find more information different rate types on Rates & Tariffs for National Grid in New York State, and Service Classification for National Grid in New York State.
- Basic Service: This is a monthly fixed amount no matter how much electricity you consume. It includes the cost for reading and maintaining the meters, billing, equipment and maintenance.
- Delivery: This is the charge to bring the electricity from the electricity production site to your home. This is not a supply cost since it is the same regardless of your supplier.
- Incremental state assessment: Also called the Temporary New York State Surcharge, it is created to encourage the conservation of energy and other resources provided through utility companies.
- SBC (state surcharge): The System Benefits Charge incentivizes energy efficiency initiatives, education and outreach, R&D, and energy assistance for people with low-income.
- RPS (state surcharge): The Renewable Portfolio Standard incentivizes renewable energy goals set by the state of New York.
- Legacy transition charge: Customers are billed the cost or benefit of electricity supply agreements National Grid signed before June 1, 2001. Residential customers also receive the benefit of low cost hydropower and a discount payment from the New York Power Authority.
- RDM: Revenue Decoupling Mechanism: National Grid makes yearly previsions on the revenues associated with the delivery service to customers. If the targets for delivery revenues are reached, then the surplus is refunded to the customer, and if the targets are not reached, the lack is collected from the customers.
- Transmission Revenue Adjustment: This is identical to the RDM, but for the transmission revenues. If the targets for the revenues associated with the transmission of the electricity are reached, the surplus is refunded to the customer, and if not, the lack is collected from the customers.
- Tariff Surcharge: New York State and many local municipalities impose taxes on National Grid's revenue. These costs are recovered through a tariff surcharge and may vary depending on the municipality.
- Sales Tax: In some areas National Grid is required to collect state and local sales taxes for the sales of electricity.
Gas delivery
- Meter information: This resumes the gas meter reading: dates of current and last meter reading and number of days, volume (in ccf) shown on current and last meter reading, conversion factor between volume (ccf) and energy (therm), and calculated number of therms used.
- Rate: Gas SC1 Residential Heat: Indeed, the electric service is SC1 non heat, since the gas takes care of the heat portion of the home energy needs. You can find more information different rate types on Rates & Tariffs for National Grid in New York State, and Service Classification for National Grid in New York State.
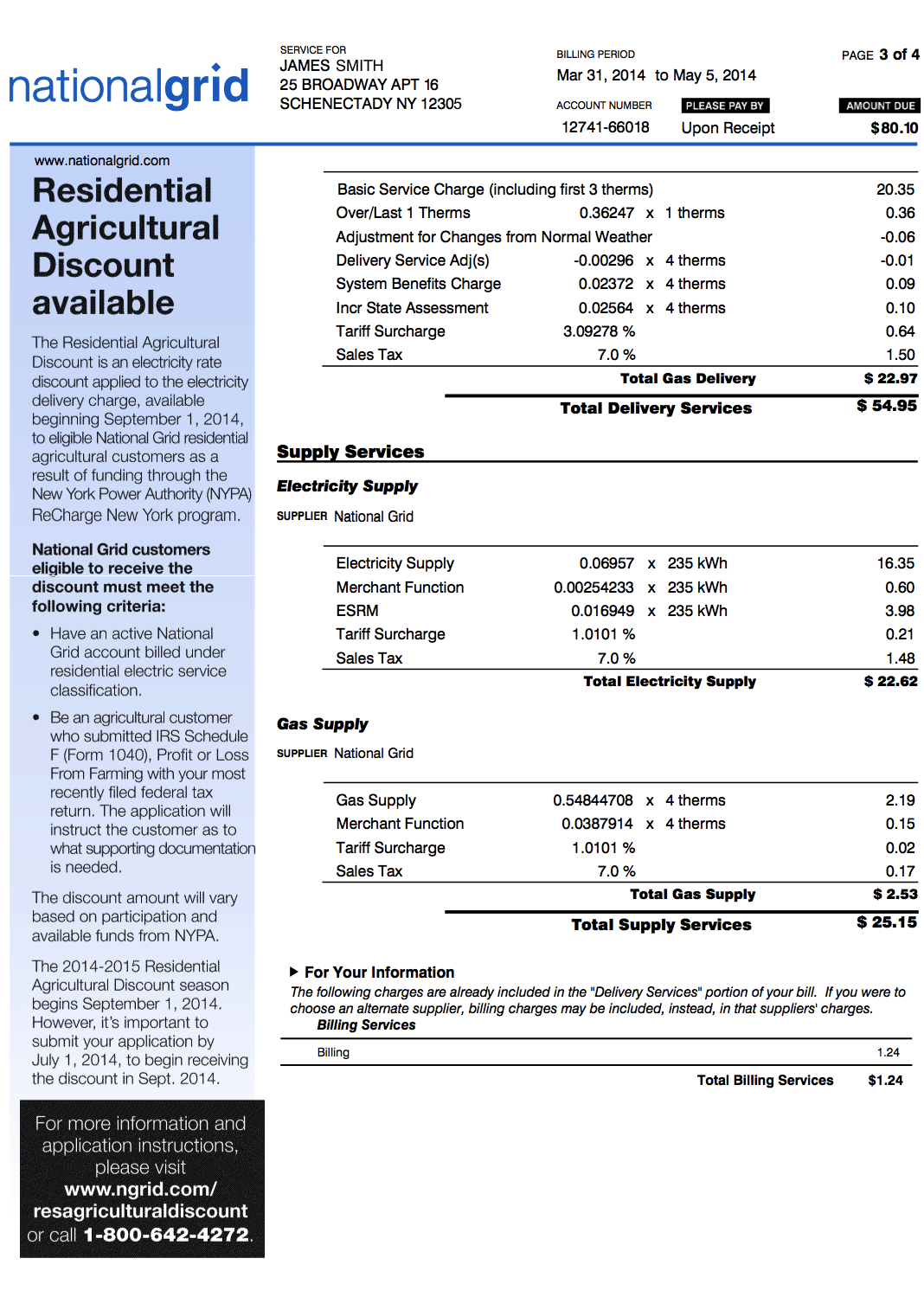
Example of a 2014 National Grid bill - page 3
Gas Delivery (continued):
- Basic Service Charge: This is a monthly fixed amount after the first 3 therms you consume. It includes the cost for reading and maintaining the meters, billing, equipment and maintenance.
- Over/Last 1 Therms: This is the Delivery Service Charge for the rest of your gas consumption after the first 3 therms. In this example, the customer has only consumed 4 therms in total, therefore this charge will only count 1 therm.
- Adjustment for Changes from Normal Weather: This is the same as the charge called "Monthly rate adjustment" in other utilities (ConEdison for example). This charge adjusts the customer's gas bills due to variations from normal weather during the cold months (October through May).
- Delivery Service Adjustment(s): This charge is either collected or returned to the customer and includes a Pipeline Refund, Net Revenue Sharing Adjustment, Research & Development Surcharge, Revenue Decoupling Mechanism Adjustment, and Deferral Credit.
- System Benefits Charge: This is a charge pay for certain public policy programs such as energy efficiency.
- Incremental State Assessment Surcharge: (Also called Temporary New York State Surcharge) created to encourage the conservation of energy.
- Tariff Surcharge: charges which pays for State and municipal tax imposed on National Grid's revenue.
- Sales Tax: state and local sales tax for the sales of gas.
Supply Services
Electricity Supply
- Electricity Supply: The market price of electricity supply used during the billing period.
- Merchant Function Charge: A charge for the Company's cost to procure gas or electricity supply. The Company will not bill you this charge if you choose an alternate supplier.
- The Electricity Supply charge together with the Merchant Function Charge can be compared with alternate supplier offers to get the best deal for electricity (and gas).
- ESRM: Electricity Supply Reconciliation Mechanism: In winter months colder than the average winter, the market prices of electricity rise due to high demand. The bills for residential customers can see great increase, since both the price of electricity, and the demand in electricity increase. The Public Service Commission of New York State has agreed to allow National Grid to spread out this bill increase. Therefore during a very cold month you will see this ESRM charge as a negative charge, in reality lending you money to avoid paying a high bill during an unusually cold month, and will reimburse this loan by surcharging you during the following months.
- Tariff Surcharge: See definition above.
- Sales Tax: Same as above definition.
Gas Supply
- Gas Supply: This pays for National Grid to purchase the gas from suppliers, and also to transport the gas to National Grid's distribution system. If you choose an alternate supplier, the price will be what you agree upon with that supplier.
- Merchant Function: See definition above.
- Tariff Surcharge: See definition above.
- Sales Tax: See definition above.
For Your Information
- Billing Services: these are the charges to create and send your bill, as well as process your payment. They are already included in the delivery portion of your bill, but are here for your information. If you choose an alternate supplier, it may in some cases pay for the billing services, in which case it would be included in the supplier's charges of the alternate supplier.
Example of a 2014 National Grid bill - page 4
Definitions:
- This pages gives you a definition of each part of your bill.